Which of the Following Best Describes Graft Versus Host Disease
Graft-versus-host disease GvHD is a complication of an allogeneic stem cell or bone marrow transplant in which cells from a donor trigger an autoimmune-like response in the recipient causing the body to attack its own tissues. Which of the following best describes graft-versus-host disease.

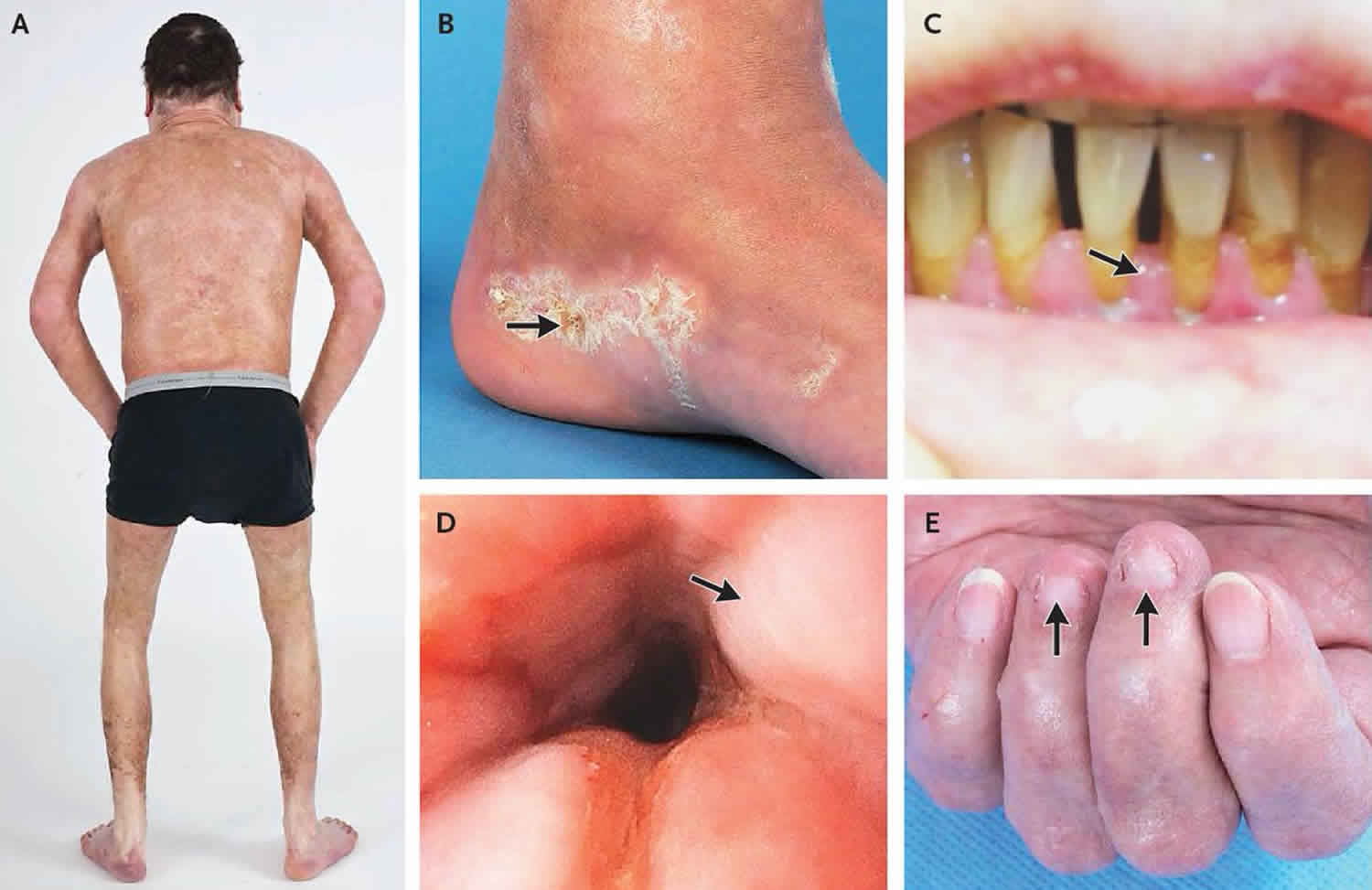
Oral Graft Versus Host Disease A Pictorial Review And A Guide For Dental Practitioners Elad International Dental Journal Wiley Online Library
Graft versus Host Disease GVHD is a rare disorder that can strike persons whose immune system is deficient or suppressed and who have received a bone marrow transplant or a nonirradiated blood transfusion.

. Immune cells in transplanted bone marrow attack the cells of the host. GVHD can also be helpful because the donors cells also attack the cancer more vigorously. An allogeneic transplant is one in.
1 Acute GVHD describes a distinctive syndrome of dermatitis see the image below hepatitis and enteritis developing within 100 days after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation HCT. Transfusion-associated graft-versus-host disease ta-GVHD is a rare and usually fatal complication of blood transfusion in which lymphocytes from the transfused blood component attack the recipients tissues especially the skin bone marrow and gastrointestinal tract. Graft-versus-host disease GVHD is the major cause of morbidity and non-relapse mortality in patients after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation HCT.
Cutaneous manifestations are the earliest and most common presentation of the disease. Graft-versus-host GVH disease can occur when _____. Graft versus host disease GVHD is an immune-mediated condition resulting from a complex interaction between donor and recipient adaptive immunity.
The graft MUST be capable of recognizing foreign Ag on host tissue. The disease is a side effect that is common after an allogeneic bone marrow transplant stem cell transplant. B bone marrow transplant.
The most common tissues attacked are the skin liver eyes lungs immune system musculoskeletal system and the gut. This article describes the pathophysiology clinical presentation diagnosis and treatment options available for acute and chronic GVHD. White blood cells of the donors immune system which remain within the donated tissue recognize the recipient as foreign.
Graft-versus-host disease is a syndrome characterized by inflammation in different organs. Recognition is often delayed because nonspecific symptoms are attributed to the. Symptoms may include skin.
High-dose chemotherapy radiotherapy inflicts cellular damage and this leads to an inflammatory process. Acute graft versus host disease aGvHD. There are two forms of GvHD.
The white blood cells present within the transplanted tissue then attack. With graft-versus-host disease graft refers to a section of transplanted or donated tissue like bone marrow or peripheral blood and host refers to the tissues of the person receiving the transplant. Graft-versus-host disease will most likely be a complication of an A skin graft.
GvHD is commonly associated with bone marrow transplants and stem cell transplants. T and B cells are transplanted Following an organ transplant therapeutic immunosuppression to prevent organ rejection may be accomplished by any of the following EXCEPT __________. Graft versus host disease GvHD is a condition that might occur after an allogeneic transplant.
The recipient MUST be incapable of. GVHD refers to multi-organ syndromes of tissue inflammation andor fibrosis that primarily affect skin gastrointestinal tract liver lungs and mucosal surfaces. Graft-versus-host disease GVHD is an adverse immunologic phenomenon following allogenic hematopoietic stem cell transplant.
Host Disease GVHD when the transplanted killer T-cells attack the recipients tissues. The graft MUST contain immunocompetent alloreactive T cells. Graft-versus-host disease GVHD is an immune condition that occurs after transplant procedures when immune cells from the donor known as the graft or graft cells attack the recipient patient hosts tissues.
Acute graft-versus-host disease aGvHD occurs following an allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplant and is a reaction of donor immune cells against host tissues and remains a major cause of morbidity and mortality Greinix 2008. Immune cells attack transplanted tissue in a privileged site. Chronic graft versus host disease cGvHD.
A tissue transplant is rejected because the hosts T cytotoxic cells are activated and kill the transplanted tissue. In graft versus host disease immune cells in. Graft-versus-host disease GvHD is a complication of a stem cell or bone marrow transplant in which cells from a donor regard the tissues of the recipient as foreign and launch an immune assault triggering a host of potentially serious symptoms.
In GvHD the donated bone marrow or peripheral blood stem cells view the recipients body as foreign and the donated cellsbone marrow attack the body.

Figure 1 From Graft Versus Host Disease Part I Pathogenesis And Clinical Manifestations Of Graft Versus Host Disease Semantic Scholar

Figure 14 From Graft Versus Host Disease Part I Pathogenesis And Clinical Manifestations Of Graft Versus Host Disease Semantic Scholar

Peach Banana Green Smoothie Tasty Balance Nutrition Los Angeles Registered Dietitian Nutritionist Recipe Heart Pictures Stock Images Free Graft Versus Host Disease

Rehabilitation Interventions In The Multidisciplinary Management Of Patients With Sclerotic Graft Versus Host Disease Of The Skin And Fascia Archives Of Physical Medicine And Rehabilitation

Figure 7 From Graft Versus Host Disease Part I Pathogenesis And Clinical Manifestations Of Graft Versus Host Disease Semantic Scholar

Skin Lesion Of Chronic Graft Versus Host Disease The Maculopapular Download Scientific Diagram

Graft Versus Host Reaction An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Oral Graft Versus Host Disease A Pictorial Review And A Guide For Dental Practitioners Elad International Dental Journal Wiley Online Library

Acute Graft Versus Host Disease From The Bench To The Bedside Semantic Scholar

Cutaneous Chronic Graft Versus Host Disease Following Allogeneic Haematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation In Children A Retrospective Study Html Acta Dermato Venereologica

Chronic Graft Versus Host Disease Gvhd In Children Semantic Scholar

Clinical Pathologic Classifi Cation Of Chronic Graft Versus Host Download Scientific Diagram

Graft Versus Host Disease Sciencedirect

Graft Versus Host Disease Part I Pathogenesis And Clinical Manifestations Of Graft Versus Host Disease Semantic Scholar

Severity Of Acute Graft Versus Host Disease Download Table

Cutaneous Chronic Graft Versus Host Disease Following Allogeneic Haematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation In Children A Retrospective Study Html Acta Dermato Venereologica

Graft Versus Host Disease Gvhd The European Blood And Marrow Transplantation Textbook For Nurses Ncbi Bookshelf
Graft Versus Host Disease Causes Signs Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment

Diagnosis And Manifestations Of Chronic Graft Versus Host Disease Semantic Scholar
Comments
Post a Comment